Report Shows MCAA Members Don’t Invest Enough in Tech Budget and Manpower
In 2018, MCAA sponsored a JBKnowledge Construction Technology Report that surveyed over 2,800 professionals in the construction industry. In the newly released MCAA-Focused Report, the responses given by MCAA members were separated and compared to those of the rest of the construction industry.
While MCAA members are getting heavily involved in VDC and mobile technology, they are behind the rest of the industry when it comes to some aspects of R&D. As the report’s primary researcher, Liz Beechinor from JBKnowledge points out, “Our research is showing that the construction industry as a whole is behind on R&D spending compared to other industries, but when we take a look at MCAA members’ responses and compare that to the construction industry, they are even further behind. Fewer MCAA contractors have dedicated R&D budget and employees dedicated to R&D.”
According to a 2017 McKinsey Report, the construction industry as a whole spends less than 1% of their revenue on R&D. Compared to the auto industry, which spends 3.5%, and the aerospace industry, which spends 4.5%, this can seem relatively underfunded.
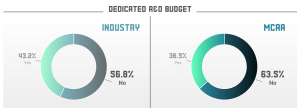
What is even more concerning is construction companies’ lack of any R&D budget. The 2018 MCAA-Focused Construction Technology Report showed that 56.8% of those surveyed had no budget for R&D, while 63.5% of MCAA members reported that they didn’t budget for R&D.
The same could be said for having employees dedicated to R&D. In the last few years, we have seen more MCAA and MSCA contractors dedicate manpower to technology research and implementation, but on average, they are still behind the rest of the industry.
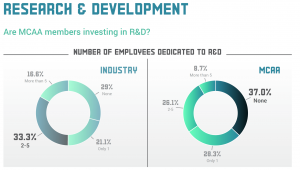 Most respondents that identified as MCAA members reported that they had one or two people dedicated to R&D, while 37% do not have employees dedicated to R&D. During a presentation on the topic at MCAA19, MCAA’s Director, Construction Technology Sean McGuire explained, “While we are seeing more members take technology seriously, smaller companies are going to always be more limited on budget and manpower that they can dedicate towards research and implementation. Larger GCs and CMs can absorb these costs a little easier simply as a function of their size.”
Most respondents that identified as MCAA members reported that they had one or two people dedicated to R&D, while 37% do not have employees dedicated to R&D. During a presentation on the topic at MCAA19, MCAA’s Director, Construction Technology Sean McGuire explained, “While we are seeing more members take technology seriously, smaller companies are going to always be more limited on budget and manpower that they can dedicate towards research and implementation. Larger GCs and CMs can absorb these costs a little easier simply as a function of their size.”
Being bigger does not necessarily mean better though. As Sean notes, “While research and staff budgets can be absorbed by larger companies easier, the bigger you are, the harder implementation becomes. Small companies can adopt changes a lot faster because you can get less people pulling in the same direction faster. Large companies have to dedicate more resources to implementation and follow up.”
This lines up with another report question that asked what the most limiting factor was for adopting new technology. Not surprisingly, lack of staff and budget received the highest response rates and were concerns for nearly half of the MCAA respondents. The report provides further insight into these questions as well as BIM productivity and estimation and mobile device and hardware use.


